
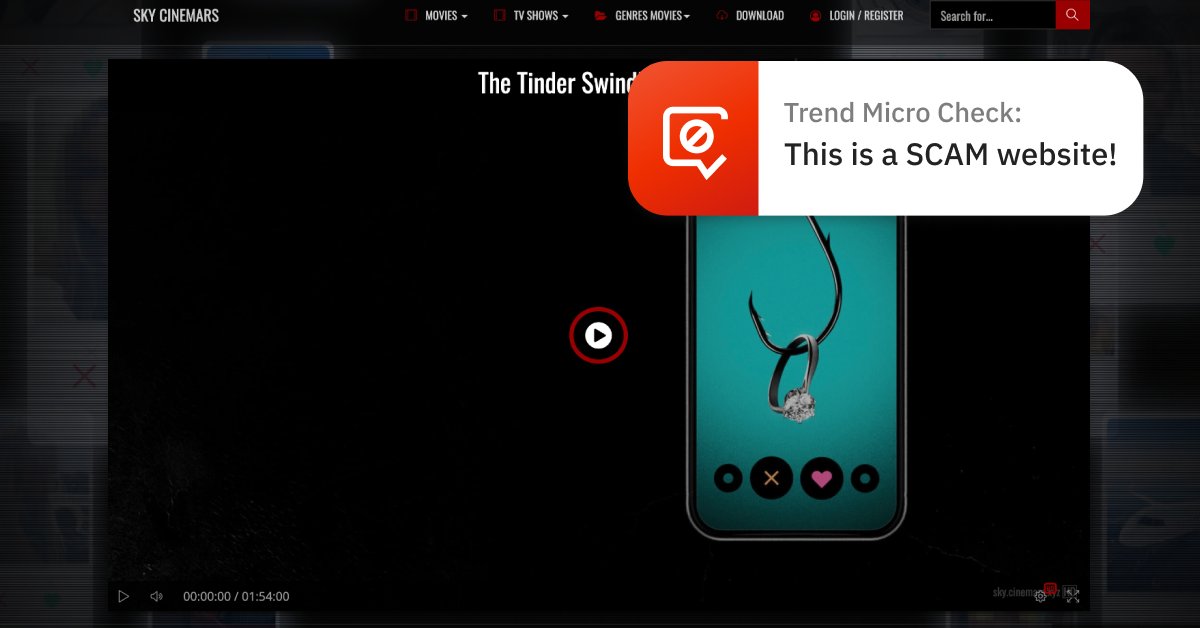
Malicious actors reportedly replaced the QR codes that users needed to scan to pay for the use of the bikes before they could be unlocked. This was the case in a scheme involving payments for bike sharing in China. People generally assume that the signs or posters with QR codes in shops and public spaces are safe, and thus might be unaware that malicious actors could replace legitimate QR codes with fake ones as part of their fraudulent schemes.
#FACEBOOK SCAM TREND MICRO DOWNLOAD CODE#
Overlaid QR codesĪ prime example of a QR code scam that relies on the physical realm is one that has malicious actors printing out QR code stickers and physically placing them over genuine ones. While cybercrime is often thought of as occurring entirely in the digital space, QR code-related threats are different in that they might partially take place in the physical realm. It’s important to note that malicious actors have invested a great deal of time and resources to making their QR code-enabled scams seem legitimate and useful, as illustrated by the following examples. So, how does one avert QR code scams? In this article, we discuss the various ways fraudsters use QR codes to deceive users and recommend tips on how users can protect themselves from QR code scams. Malicious actors seek out ordinary, unsuspecting people who don’t know much, if at all, about QR code safety. In fact, threats involving QR codes have become so rife and sly that the FBI has recently issued a warning about them. However, their popularity has also created fertile ground for malicious actors to spruce up their QR code malware toolkit to steal not only personal information but also hard-earned assets that are impossible to recover once lost. Scanning a QR code saves a user the trouble of typing out a long address in a web browser or manually entering a merchant’s username or number in a payment app, among other advantages.Ĭlearly, the convenience QR codes offer and the ubiquity of mobile devices have contributed greatly to the widespread use of these two-dimensional barcodes.

This is basically a string of text, and it’s typically a URL or link to a website or a merchant’s official account on a payment system. It can be scanned using a QR code scanner or reader, which is built into most mobile devices’ default cameras, to decipher the data that’s encoded into it. And many businesses have responded to this need through the use of quick response (QR) codes.Ī QR code is a two-dimensional barcode that can store 7,089 digits or 4,296 characters. One of the things that is likely to remain for the foreseeable future is the need for cashless and no-contact transactions.
It is thus reasonable to expect that the digital lifestyle changes precipitated by the pandemic will persist indefinitely. The practical approach, therefore, is for people to learn to live with it and do what they can to manage it. As the world eagerly hopes for the Covid-19 pandemic to end, health experts point out that the virus will not go away for good.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
